We’ve mentioned many times that SEO is a long-term activity. It usually takes several weeks or months before we start to see the results of our efforts.
But that doesn’t mean you should just sit back and wait.
Absolutely not.
During that time, we can detect signals that will tell us if we’re heading in the right direction or if, on the contrary, we need to make some adjustments to our strategy.
And to see those signals, we need to be able to measure the impact of everything we’re doing.
Want to know how I measure SEO?
In this post, I’ll talk about the so-called SEO metrics and show you which ones, in my opinion, are the most important SEO metrics for efficiently tracking your web project.
Let’s get started!

What are SEO metrics?
SEO metrics are indicators used to evaluate and measure the performance of a website, especially concerning its positioning within search engines and the effects derived from it.
Therefore, they provide objective information about the direction your web project is taking and are a fundamental basis for decision-making within any SEO strategy.
The main SEO metrics I review daily
There are a wide variety of SEO parameters that allow you to assess different aspects of your website.
There are no better or worse metrics; the use of one or another will depend on the objectives you want to achieve within your business.
Next, I’m going to show you the 7 metrics I usually pay the most attention to and that best allow me to measure the effectiveness of my actions as an SEO.
1. Organic Traffic
We start with the metric I consider the most important of all: the visits our website receives from Google.
At the end of the day, we are measuring the results of our work as SEOs, whose goal is none other than to improve our positions in search engines so that users end up reaching our website.
Therefore, the value of organic traffic and its evolution over time will tell us if we are achieving our goal or if, on the contrary, we need to rethink some aspects of our SEO strategy.
How to measure a Website’s Organic Traffic?
There are several software applications that provide information about a website’s traffic, but if you want the most accurate and reliable data, it’s best to always go to the source, that is, Google.
Google Search Console (GSC) is the essential tool that every SEO should be familiar with. In its “Performance” section, it shows us real data about the organic traffic of our domain.
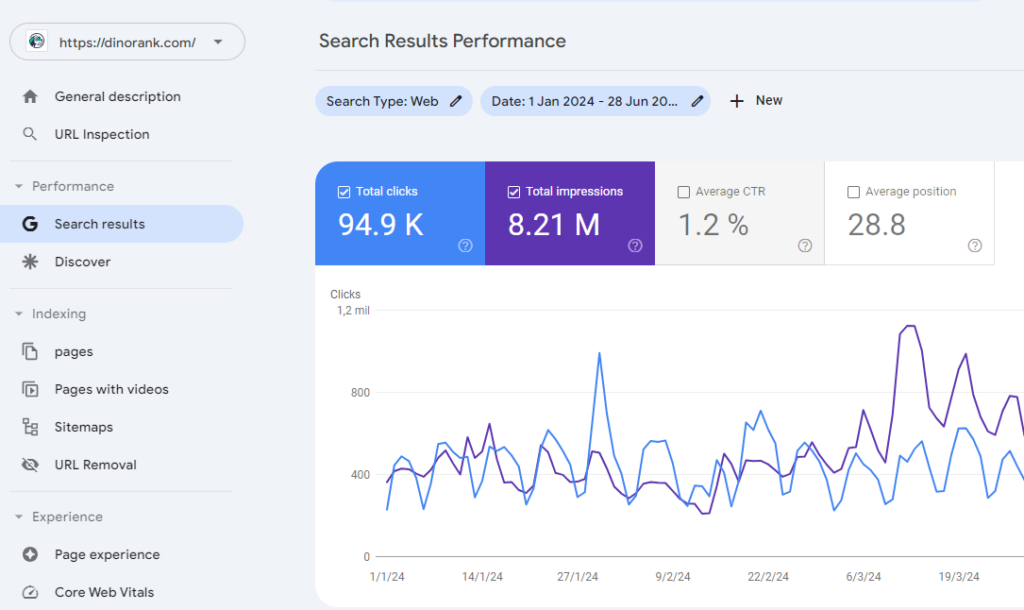
You will see a graph with the total clicks your website has received each day, as well as a table with the queries, URLs, countries, or devices that generated those clicks.
This is very valuable information that you can filter and export to a spreadsheet for more detailed analysis if you wish.
Why is this SEO metric important?
Organic traffic is an objective indicator of how relevant our content is to users. However, when analyzing this metric, you can’t just focus on its overall value; you need to pay attention to the details.
Filters by keywords, URLs, or countries are the ones that will truly indicate whether your visits reflect your actions as an SEO and have the potential to convert into sales or if, on the contrary, Google is telling you that you need to change your strategy.
2. Impressions
Impressions tell us the number of times any of the pages on your website have appeared in Google’s search results for user queries.
Maybe it’s not as important a metric as organic traffic. Just because a URL appears in the search engine doesn’t mean someone will click on it.
However, it is an indicator of a website’s visibility, especially useful in the early stages of a web project.
It’s not typical for a URL to show up in Google’s Top 1 right off the bat; instead, it usually starts appearing in the Top 20, then within the Top 10, and gradually climbs up the ranks over time.
Impressions allow us to evaluate this trend and verify that our website, despite not receiving many clicks yet, is starting to gain a foothold in the SERPs.
How to Measure Website Impressions
Once again, Google Search Console is the best tool you have to evaluate the impressions of your website.
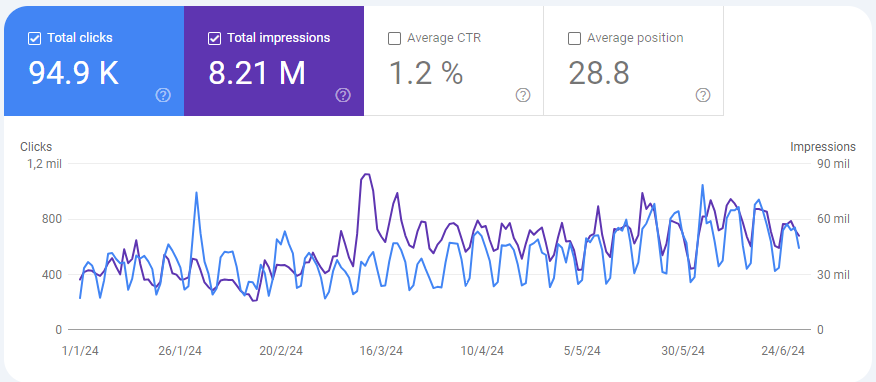
If you look at the graph above, you’ll see that GSC also offers you two other metrics:
- Average CTR, which is the percentage of impressions that generated a click.
- Average position where your pages appear within the SERPs.
Along with organic traffic and impressions, these two measures are also very helpful when analyzing your website’s performance.
Why is this SEO metric important?
You should always analyze the value of impressions in conjunction with your traffic.
If your website appears many times on Google, but the clicks are lower than expected (the CTR is very low), something might be wrong.
You might need to improve your meta titles and meta descriptions to make them more attractive and encourage users to click on your site.
It’s also possible that you need to optimize your content to move up in the rankings for the keywords where the search engine is already valuing you.
3. Keyword Ranking
One of the usual tasks of an SEO involves conducting in-depth research on the keywords most used by users when making queries on search engines.
However, it’s difficult to know if your Keyword Research is correct if you don’t track the evolution of the keywords you want to rank for.
We’ve already seen before that Google Search Console shows you the keywords that have impressions and receive clicks. But many of these keywords might not be the ones you are most interested in knowing about.
Several of them may even have ranked by chance, without you intending it. Therefore, if you want to monitor your keywords professionally, it’s best to use an SEO tool specialized in this function.
How to Measure the Evolution of a website’s Keywords
To do a detailed tracking of the keywords I’m interested in ranking in each of my projects, the SEO tool I use in my work is DinoRANK.
Thanks to its position tracker, I can define which are the most important keywords for my websites and track their daily evolution within the SERPs.
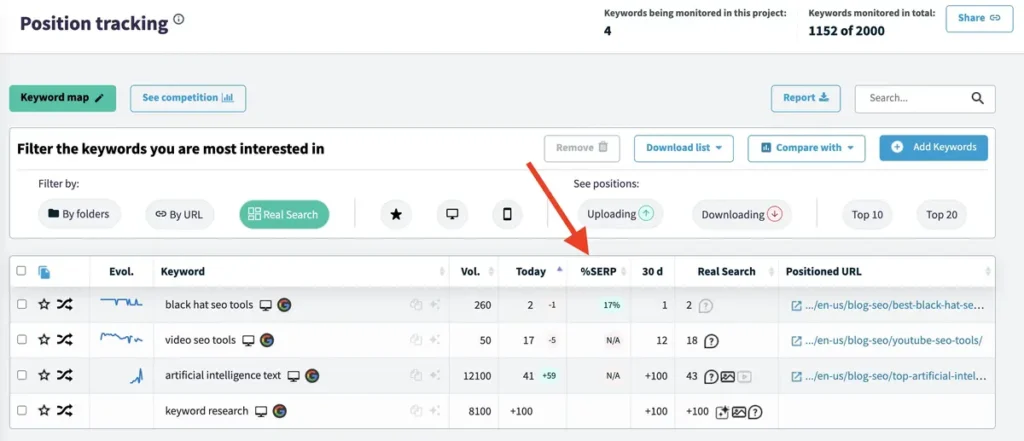
DinoRANK will tell you the real visibility of that keyword, as it is able to show the % of scroll you have to do within the Google SERP, until you reach your organic result.
Finally, you can also see your position today in the organic SERP and also your current position within the AI Overviews, in case you appear in them.
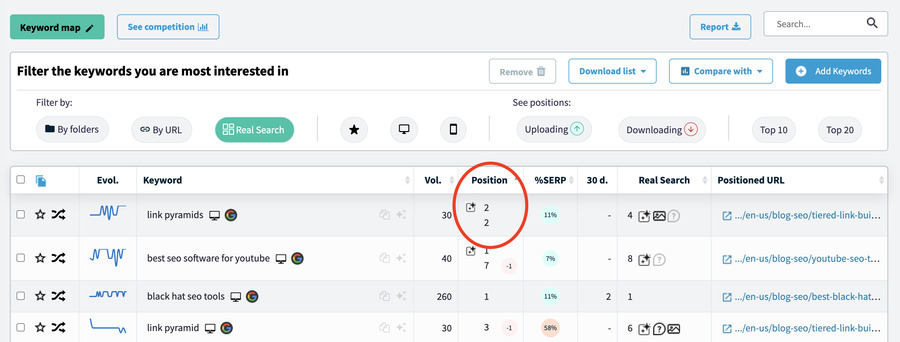
Generally, informational keywords are easier to rank for, so in the early stages of a project, I usually focus on them. As they start to rank and the website gains authority, business keywords begin to take center stage.
Try DinoRANK right now!It’s then time to focus efforts on this other group of much more transactional keywords.
As you can see, having the right SEO tool not only allows us to track metrics but also to adjust the information to our needs and make decisions focused on different objectives.
Why is this SEO metric important?
Monitoring keywords will indicate how relevant our website is to Google when it tries to answer the most important queries within our business.
Moreover, it allows us to detect errors in our strategy, such as keyword cannibalization. Thanks to SEO tools like DinoRANK, you can find out if multiple URLs on your site are competing for the same keyword and adjust your content to fix it.
4. Indexed Pages
Keep this in mind: if you want your pages to rank, you must make sure Google has them indexed.
And it’s not enough to check it once and forget about it, as Google tends to deindex certain pages from time to time.
Therefore, my advice is to get into the habit of checking this metric periodically. Especially if you notice that your traffic or impressions drop unexpectedly.
How to Measure a Website’s Indexed Pages
Within Google Search Console, you can easily check the indexing status of your website’s URLs.
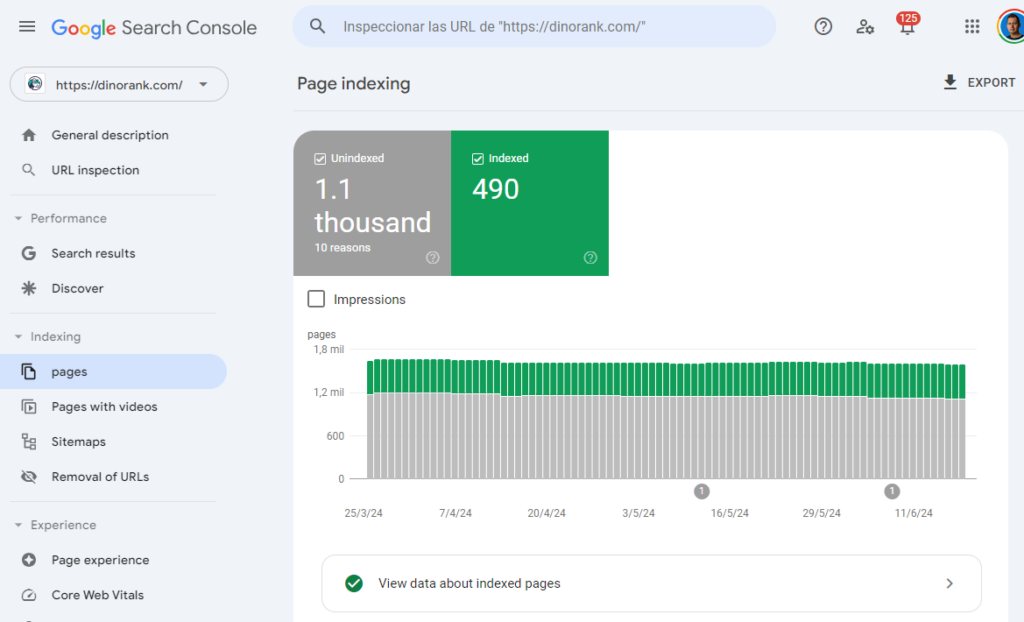
You’ll see which pages are indexed and which are not. Additionally, you will know the reason preventing Google from indexing a particular URL and, if you wish, you can request its indexation again so you don’t have to wait for Google’s crawlers to decide to re-inspect your site.
Why is this SEO metric important?
For a URL to appear in Google’s results, its search engine must first crawl it and add it to its index.
Knowing which pages are not being indexed allows us to detect errors such as crawl blocks, incorrect use of the noIndex tag, as well as the existence of duplicate or low-value content (thin content) that we need to correct.
5. Traffic by URL
Earlier, we talked about organic traffic and how you can measure it.
However, it’s not the same if most of the traffic comes from a single URL compared to being distributed among several of them.
It’s also different if the visits are going to your most transactional pages versus most of your users landing on informational articles that don’t have a commercial objective.
Knowing the exact destination of the traffic you capture from Google will allow you to make informed decisions about the actions you need to take to improve your results.
For instance, if within the set of URLs you are working on, there is a group that is ranking above average and belongs to a specific cluster or category, it might be worth diving deeper into that cluster content-wise, because it’s a topic for which Google is already giving you authority.
Similarly, if you know which pages are bringing you the most visits, you can try to improve internal linking and the copy of your articles to direct them to more commercial sections, with the goal of increasing your sales.
How to Measure Traffic by URL on a Website
While Google Search Console allows you to apply filters to understand the behavior of each individual page, I don’t find it the most convenient tool for this purpose.
That’s why I usually conduct this analysis through DinoRANK. Its organic traffic module collects data from GSC and displays it in a much more user-friendly and easy-to-analyze way.
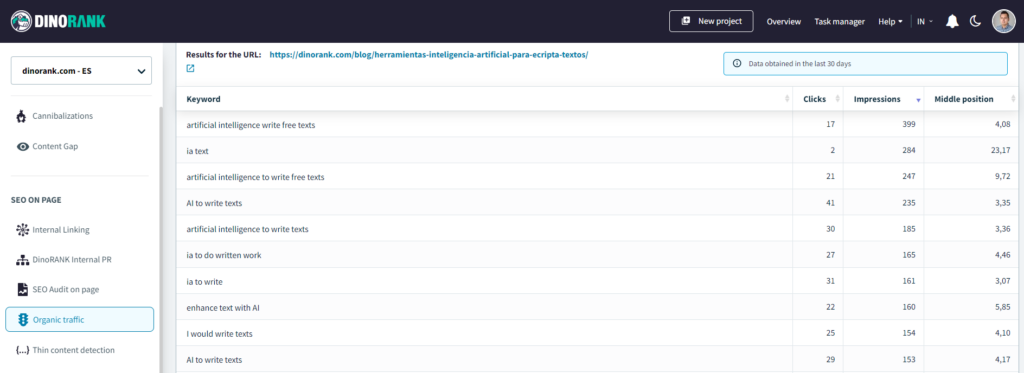
Why is this SEO Metric Important?
Knowing which pages are generating the most traffic and which are not allows us to segment our audience and better understand what type of content particularly attracts our users.
Additionally, it can help us improve navigation within our website and optimize the Calls to Action (CTA) on high-traffic pages to increase conversions.
On the other hand, knowing the URLs that Google is ranking can help us improve them to move up in the search results. There are several techniques we can apply for this, from a TF*IDF analysis, like the one conducted by DinoRANK, to optimizing internal linking to boost content within a cluster that is already being well-rated.
6. Traffic Sources
We’re still talking about traffic, but this time from a slightly different perspective.
If you work on SEO, it’s possible that most of your visits come from Google, as the main web positioning techniques focus on this search engine.
Even so, you can also receive traffic from other search engines like Bing or Yahoo, as well as direct links from other websites, social media, or paid ads.
In short, the origin of your traffic can be very varied and, depending on your strategy, you might be interested in focusing more on certain sources.
How to Measure a Website’s Traffic Sources
To see your website’s traffic sources, the most effective tool is Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Within the reports section, there’s an option called “traffic acquisition” that provides visit data grouped by their source.
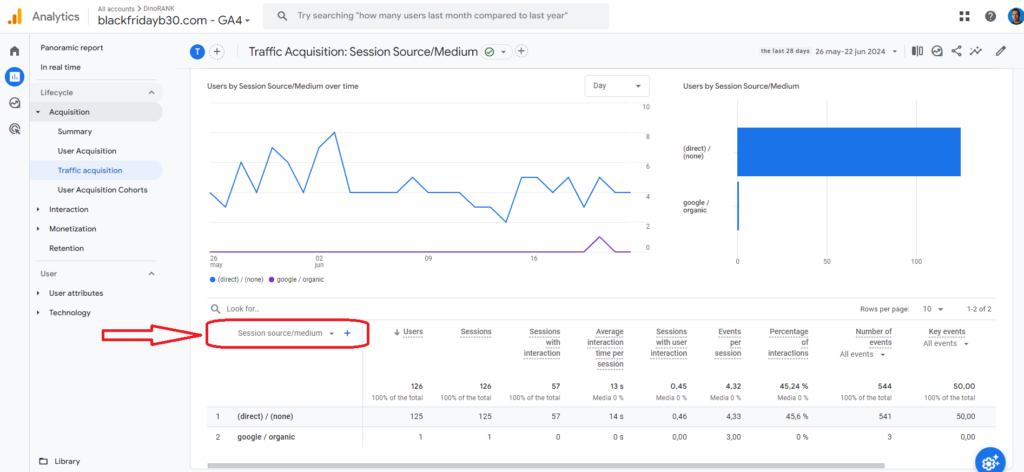
To view the information more clearly, I recommend configuring the table to show the rows based on the “Session source/medium” criterion, as indicated in the image above.
Why is this SEO Metric Important?
Measuring the performance of the different marketing channels that bring visits to our website, such as SEO, pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, social media, email marketing, direct referrals, etc., allows us to focus on those that are more effective and reduce or adjust those that are not performing well.
In short, it facilitates the efficient allocation of our resources (time, money, effort) to the channels that provide a higher return on investment (ROI).
7. Page Load Speed
The last metric I tend to pay the most attention to is the loading speed of the different pages on my websites.
That being said, I try not to obsess too much over this topic.
While it is true that the performance of a website, expressed by Google through the Core Web Vitals (CWV), is taken by the search engine as a ranking factor, experience has shown me that it is not a decisive factor.
One thing is having your website take forever to load and another is dedicating all your efforts to having a perfect score on PageSpeed.
You need to find a middle ground. I am content with offering a good user experience and making sure the website loads quickly, but I do not aim to break speed records.
How to Measure a Website’s Loading Speed
When analyzing my website’s speed, I usually use the SEO audit module from DinoRANK, which indicates the most problematic URLs in terms of slow loading.
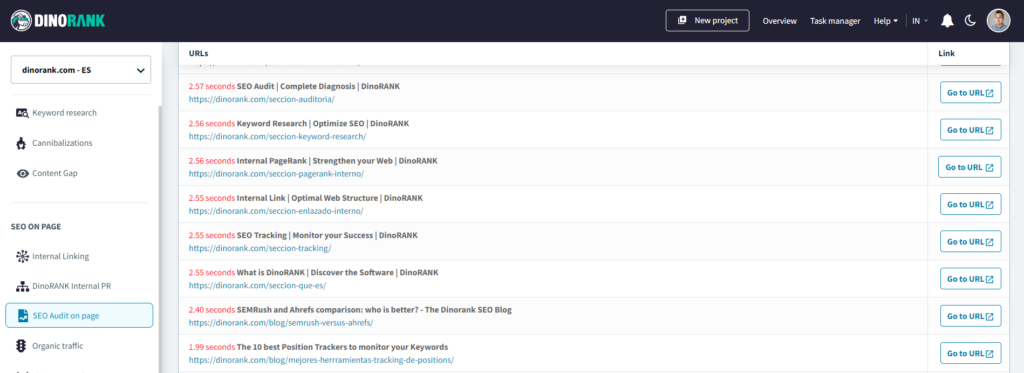
Once I identify the pages that need my attention, I perform a more thorough analysis with other specialized tools, such as Pagespeed Insights or GTMetrix, which give me more information on the specific aspects I need to improve.
Why is this SEO Metric Important?
Studies show that more than half of users will abandon your website if it takes more than 3 seconds to load.
Don’t give them this option. Monitor your page load times and ensure that your site consistently delivers adequate performance.
Conclusions
Here is my list of the SEO metrics that I use most frequently.
However, these measurements alone are not very useful. It’s not enough to collect data periodically, look at it for a while, and then forget about it. You need to interpret them correctly and act accordingly.
If you notice that a metric is below your expectations, investigate the possible causes and make the necessary adjustments to improve conversion from an SEO perspective.
This way, you will refine your strategy and see how your website improves in the rankings progressively.


2 comments
NonCon
Most website owners concentrate on checking DA/PA as they are easiest to check (and free). From time to time should check other metrics too.
What if you your site is too slow and you didn’t even know it is not loaded correctly on a visitors screen!?
Ismael Ruiz
Hi! As you say, there are times when our website does not load as fast as we would like it to. For this, I recommend you to check the loading speed with tools like GT Metrix. This way, you will be able to detect any problem before the user or client visits you.